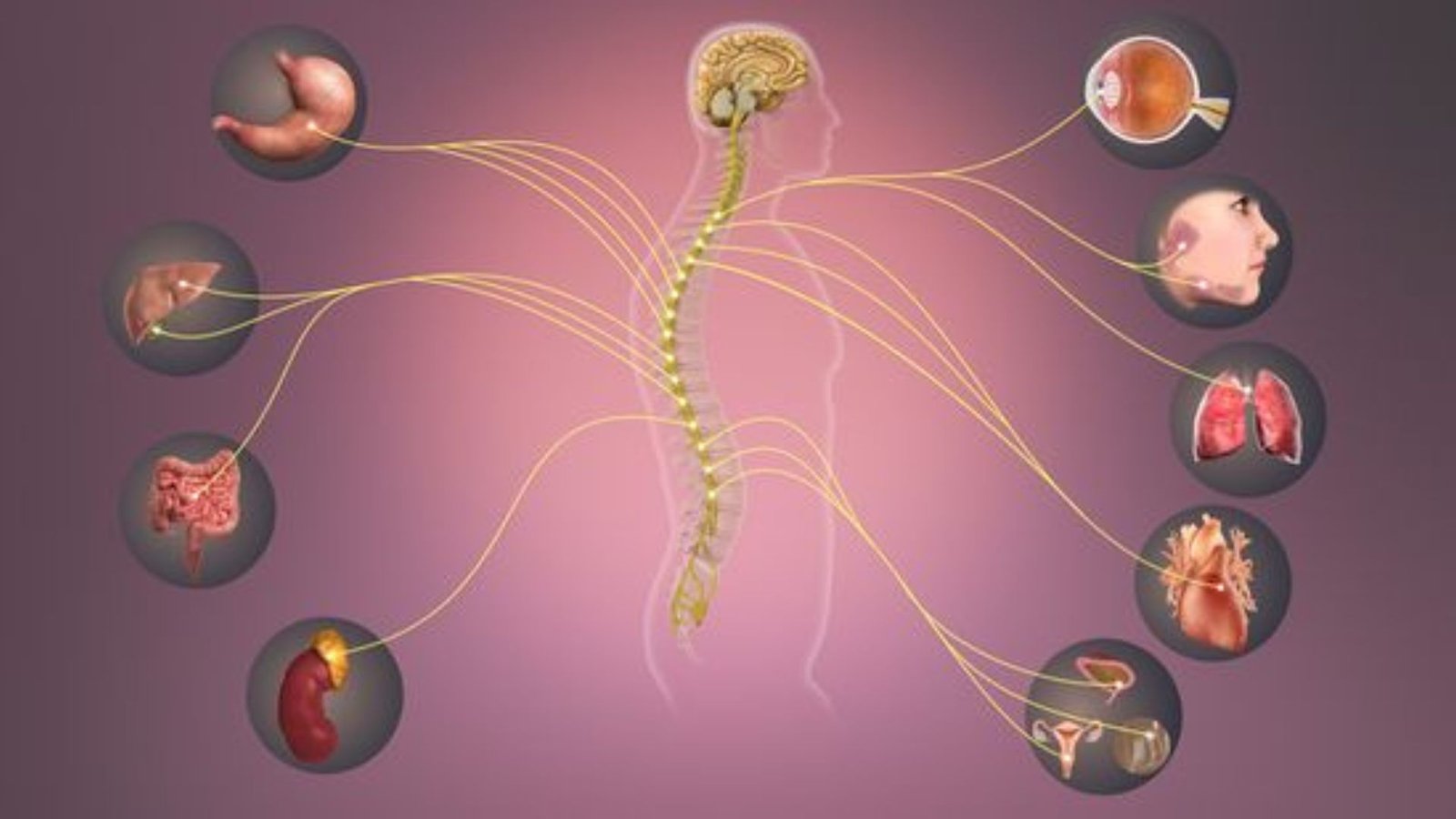
The nervous system is the body’s communication network, sending signals between the brain, organs, and muscles. These signals influence emotions, behavior, and physical responses. Understanding nervous system signals helps us interpret how our body reacts to stress, excitement, or relaxation, and allows us to respond more effectively to daily challenges.
How the Nervous System Works
The nervous system consists of two main parts:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Includes the brain and spinal cord. It processes information and sends instructions to the body.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Connects the CNS to the rest of the body, including organs, muscles, and sensory organs.
The PNS is divided into two systems:
- Somatic Nervous System: Controls voluntary movements, like walking or lifting objects, and sends sensory information to the brain.
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Controls involuntary functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and digestion. The ANS has two branches:
- Sympathetic Nervous System: Activates the “fight-or-flight” response during stress or danger.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: Promotes relaxation, recovery, and rest.
Together, these systems ensure the body responds appropriately to internal and external stimuli.
Signals and Emotional Responses
Emotions are closely linked to nervous system signals. For instance:
- Stress: When you feel stressed, the sympathetic nervous system releases adrenaline and cortisol, increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and alertness. This prepares the body to respond quickly.
- Calmness: The parasympathetic nervous system slows the heart rate and relaxes muscles, promoting feelings of safety and ease.
- Excitement or Anticipation: Nervous system signals trigger physical sensations such as butterflies in the stomach, heightened energy, or alertness.
These signals are how the body communicates emotional states, often before conscious thought catches up.
How the Body Communicates Through Signals
The nervous system uses multiple pathways to send signals, creating a language of its own:
- Muscle tension or relaxation – Tense muscles often indicate stress, fear, or anxiety; relaxed muscles suggest comfort and calm.
- Heart rate changes – A racing heart signals excitement, fear, or exertion, while a slow heart rate reflects calm and safety.
- Breathing patterns – Shallow, rapid breaths indicate stress; deep, steady breaths promote relaxation.
- Gut sensations – Butterflies or tightness in the stomach often accompany anticipation or worry.
By noticing these physical cues, we can better understand our emotions and the state of our nervous system.
Practical Ways to Tune Into Nervous System Signals
The nervous system is constantly sending signals about your emotional and physical state, but most people are unaware of these messages. Learning to tune in helps you recognize stress, excitement, or calmness early, allowing you to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively. Here are practical ways to become more aware of your nervous system signals:
Practice Body Scanning
Body scanning is a mindfulness technique where you bring attention to different parts of your body, noticing areas of tension, discomfort, or tightness. Start from the top of your head and slowly move down to your toes.
Use Mindful Breathing
Breathing is a direct bridge between the nervous system and emotional state. Slow, deep, and controlled breaths activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes relaxation and counteracts the stress response.
Observe Reactions
Pay close attention to how your body reacts in different situations. Your nervous system gives early warning signs before emotions fully surface.
Move Intentionally
Movement is a powerful tool for regulating the nervous system. Stretching, walking, yoga, or gentle exercise signals safety and helps release tension stored in muscles.
Reflect on Patterns
Tracking how your body responds to emotions over time builds awareness and emotional intelligence. Patterns reveal triggers, recurring stressors, or sources of calm.
The Connection Between Nervous System and Well-Being
Understanding nervous system signals is crucial for emotional regulation, stress management, and overall well-being. When we recognize how the body communicates feelings and reactions, we can respond with awareness rather than habit or impulse. This strengthens self-control, reduces stress, and improves relationships.
Final Thoughts
Understanding nervous system signals shows that emotions and bodily reactions are deeply interconnected. The body constantly sends signals through heart rate, muscles, breathing, and gut sensations. By paying attention to these signals, we gain insight into our emotional state, make better decisions, and respond to life with more balance and clarity.