Haptonomie, a lesser-known field, focuses on the science of affectivity. It examines how touch influences emotional and physical well-being. This therapeutic approach traces the development of haptonomie, its origins to the mid-20th century. Dutch physiotherapist Frans Veldman founded it, introducing unique techniques. Veldman believed touch could profoundly impact human connections and overall health.

Origins of Haptonomie
In the 1940s, Veldman began exploring the effects of touch on patients. His experiences during World War II deeply influenced his ideas. He noticed how gentle, empathetic touch could alleviate pain and anxiety. Veldman hypothesized that touch played a crucial role in human communication. He developed a theoretical framework, emphasizing affectivity and contact.
Development in the 1950s and 1960s
Throughout the 1950s and 1960s, Veldman refined his methods. He conducted extensive research and documented his findings meticulously. Veldman introduced Haptonomie as a formal discipline, attracting attention from healthcare professionals. His approach gained traction, particularly in the Netherlands and Belgium. Practitioners began integrating Haptonomie into their therapeutic practices.
Key Principles of Haptonomie
Haptonomie revolves around several key principles. Central to this practice is the concept of affective touch. This involves using touch to communicate empathy and support. Practitioners believe that affective touch can foster emotional connections, reduce stress, and promote healing. Another principle is the emphasis on presence and attunement. Practitioners aim to be fully present with clients, tuning into their emotional states.
Expanding Influence in the 1970s and 1980s
In the 1970s and 1980s, Haptonomie continued to expand. Training programs were established to educate new practitioners. Veldman’s teachings spread beyond the Netherlands, reaching France, Germany, and other European countries. Medical professionals began incorporating Haptonomie into obstetrics, palliative care, and psychotherapy. The field gained recognition for its holistic approach to health.
Modern Applications of Haptonomie
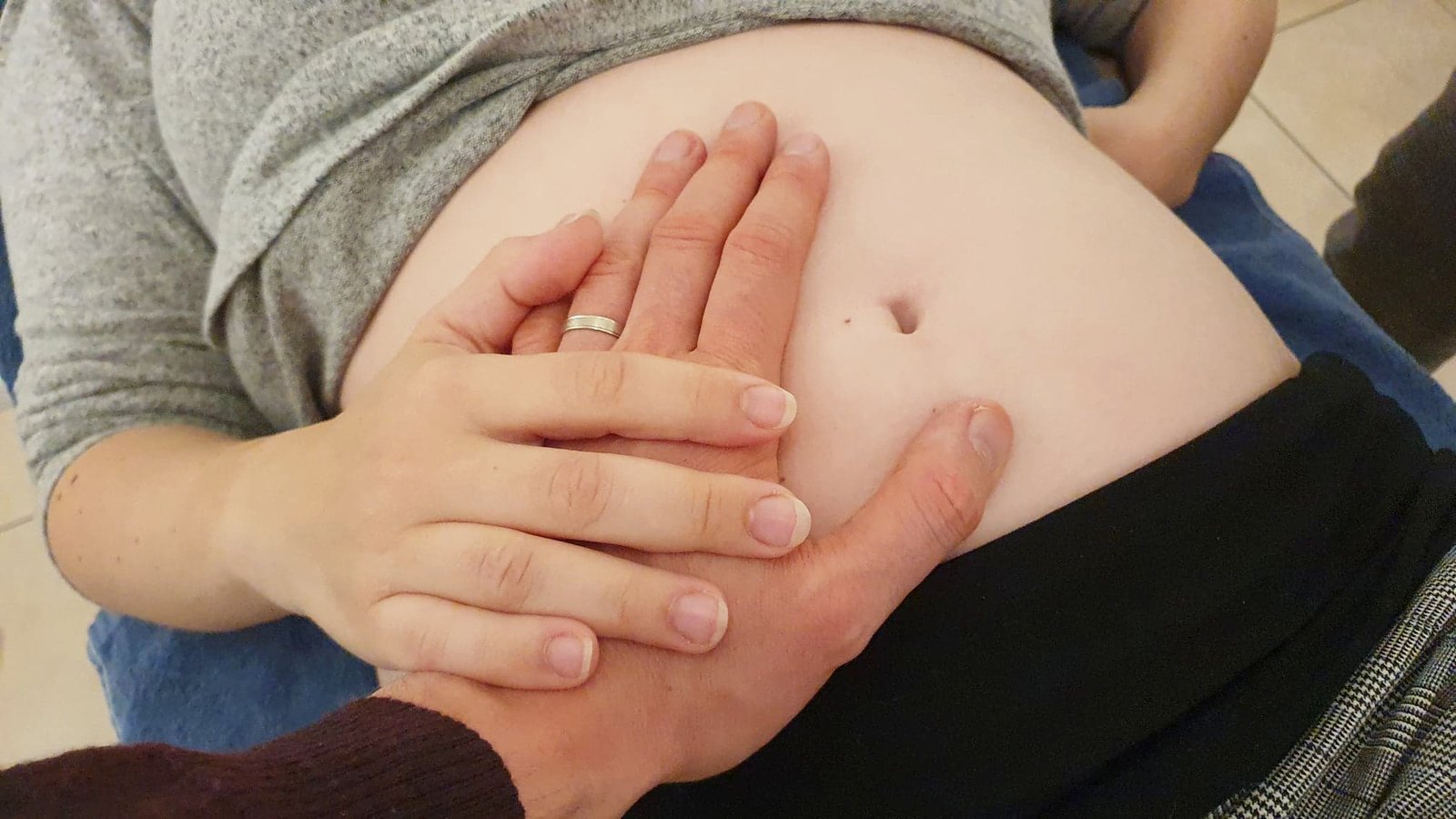
Today, Haptonomie has diverse applications. It is used in prenatal care to enhance bonding between parents and unborn children. Haptonomie can also support individuals facing chronic illness or terminal conditions. By focusing on affective touch, practitioners aim to provide comfort and emotional support. Additionally, therapists use Haptonomie to address psychological issues, fostering trust and safety.
Training and Certification
Aspiring Haptonomie practitioners undergo rigorous training. Programs typically include theoretical coursework, practical training, and supervised practice. Certification requirements vary by country, ensuring practitioners meet professional standards. Training emphasizes the importance of ethical considerations, respect, and empathy. Practitioners must maintain a high level of sensitivity and attunement to clients’ needs.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its benefits, Haptonomie faces challenges and criticisms. Skeptics question the scientific validity of its principles. Limited empirical research exists to support its effectiveness. However, many practitioners and clients report positive outcomes. The subjective nature of affective touch makes it difficult to measure objectively. Despite this, Haptonomie continues to gain acceptance in various therapeutic settings.
Future Directions
The future of Haptonomie holds promise. Researchers are exploring ways to integrate it with other therapeutic modalities. There is a growing interest in studying its effects on mental health and well-being. As awareness of Haptonomie increases, more healthcare professionals may incorporate it into their practice. Continued research and documentation will be crucial in establishing its efficacy.
Conclusion
Haptonomie, rooted in the pioneering work of Frans Veldman, has evolved into a respected therapeutic approach. Its emphasis on affective touch and emotional attunement offers unique benefits. While challenges remain, its potential to enhance well-being is undeniable. As the field progresses, Haptonomie may play an increasingly significant role in holistic healthcare.




I think this internet site contains very great composed written content blog posts.